TOP CATEGORY: Chemicals & Materials | Life Sciences | Banking & Finance | ICT Media

Download Report PDF Instantly
Report overview
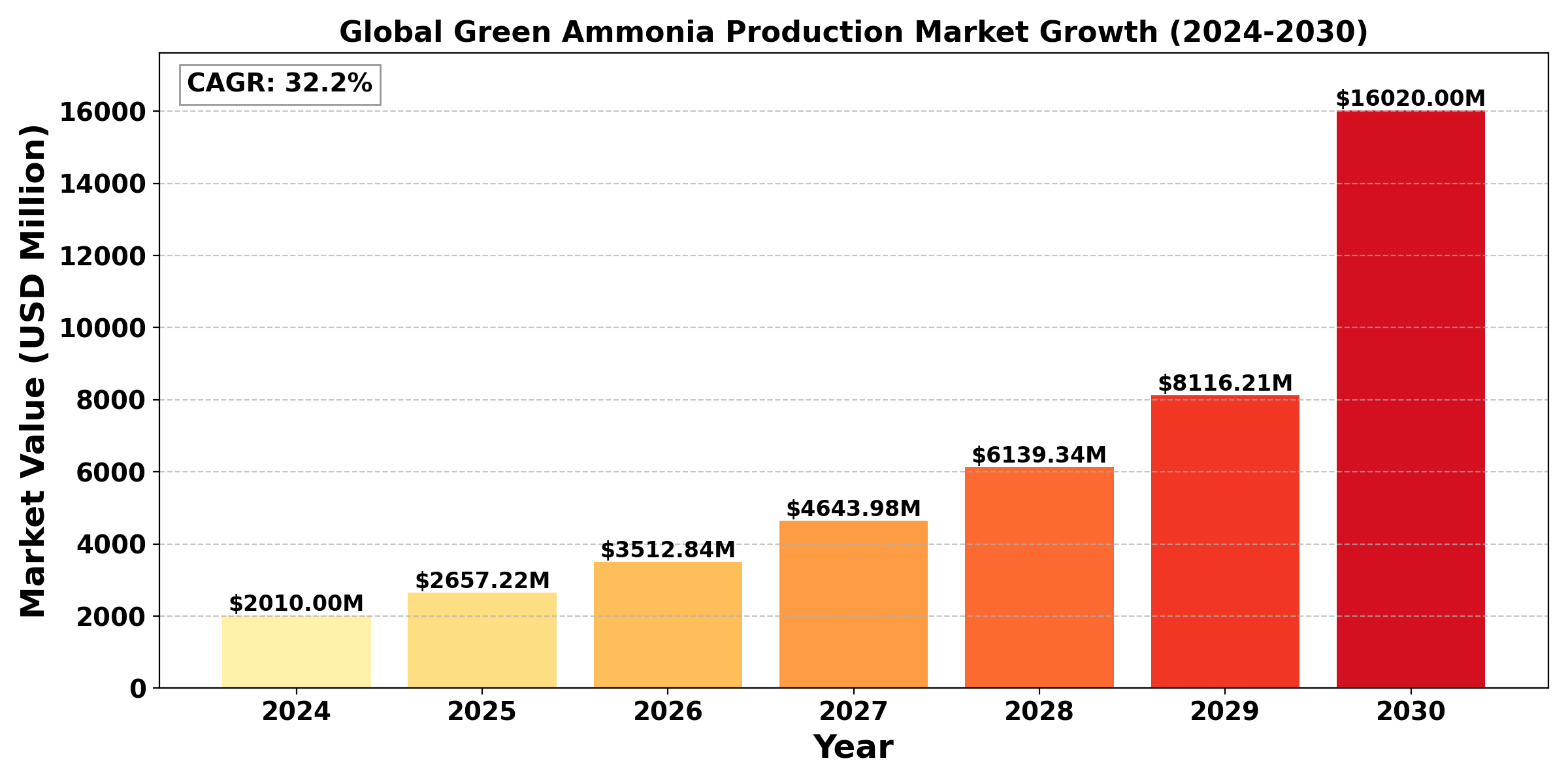
The "Global Green Ammonia Production Market" was valued at US$ 2.01 Billion in 2024 and is predicted to reach US$ 16.02 Billion by 2030, exhibiting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 32.2% during the forecast period (2023-2030).
Decarbonizing ammonia production and lowering greenhouse gas emissions are the driving forces behind the expanding green ammonia production market. High carbon emissions are a by-product of traditional ammonia production, which mostly uses the Haber-Bosch process and fossil fuels like natural gas. Green ammonia production, on the other hand, employs renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro to electrolyze water and produce hydrogen, which is then mixed with nitrogen to produce ammonia. Green ammonia is a desirable alternative for sustainable agriculture, where ammonia is frequently used as a fertilizer, as well as for industrial uses because this technique drastically lowers or eliminates carbon emissions.
As a carbon-free substitute for traditional marine fuels, green ammonia is also gaining popularity as a possible clean fuel, particularly in the maritime sector. In sectors where electrification is difficult, green ammonia is positioned as a crucial alternative as countries and companies strive toward net-zero emissions. With the help of company sustainability programs, government legislation, and incentives, investment in green ammonia projects has increased. High production costs, limited infrastructure, and the requirement for extensive renewable energy sources are some of the market's obstacles. Partnerships in the energy, agricultural, and logistics industries are anticipated to increase its market reach, while technological developments and economies of scale are anticipated to increase cost-effectiveness. Overall, the green ammonia market holds significant potential as a cornerstone of the green hydrogen economy and a critical component in the global shift towards carbon neutrality
➣ Segmental Overview
Alkaline Water Electrolysis (AWE) to hold the highest market share: By Type
Alkaline Water Electrolysis (AWE) is currently the electrolysis technology with the largest market share in the worldwide green ammonia production market. AWE is a popular option for green ammonia projects because it is a well-established and mature technology. In comparison to more recent options like PEM WE and SOE, it has been utilized in the generation of hydrogen for decades and has the advantages of a simpler setup, shown dependability, and comparatively lower costs. AWE is more economical for large-scale green ammonia plants because of these factors, especially in applications where electricity costs from renewable sources are a significant consideration
Shipping fuel to hold the highest market share: By Application
Shipping fuel is anticipated to have the highest market share among applications in the worldwide green ammonia production market in, followed by carbon fixation, hydrogen storage, and hybrid power generation. Due to the marine industry's increasing decarbonization and the strict emissions requirements imposed by the International Marine Organization (IMO), green ammonia has become a popular shipping fuel. Since ammonia is a zero-carbon fuel that can be used in fuel cells and internal combustion engines, it presents a competitive alternative to conventional marine fuels and aids in reducing emissions in a hard-to-electrify industry.
Another crucial use for green ammonia is hydrogen storage, which offers a reliable and effective means of storing and moving hydrogen across great distances. In global hydrogen supply chains, green ammonia's capacity to function as an energy carrier and move hydrogen from renewable production hubs to consuming locations is valuable.
By turning captured CO₂ into useful chemicals, carbon fixation—a possible application—helps industry lower their carbon footprints. Green ammonia is utilized in carbon capture and utilization (CCU) processes. Finally, a smaller but expanding market is hybrid power generation, which blends green ammonia with renewable energy. In this case, ammonia can offer dependable backup power for renewable energy sources, guaranteeing consistent energy production and promoting grid stability.
➣ Regional Analysis
The market for green ammonia production is growing in different ways in different locations due to factors like industry demand, government backing, and the availability of renewable energy. Europe is the market leader thanks to its aggressive climate goals, strict carbon reduction regulations, and large investments in infrastructure for renewable energy. Green ammonia projects are being established by nations such as Germany, the Netherlands, and Denmark, mainly for use as fertilizer and as a clean fuel in naval applications. Another important location is Asia-Pacific, where South Korea and Japan are using green ammonia first for energy diversification and hydrogen storage in order to become carbon neutral. Furthermore, Australia is becoming a significant producer of green ammonia, utilizing its wealth of solar and wind energy for extensive export initiatives.
In order to decarbonize industrial processes and incorporate green ammonia into its hydrogen strategy, the United States is investing in green ammonia in North America through private sector initiatives and legislative incentives. In the meantime, Middle Eastern nations—Saudi Arabia in particular—are using the potential of solar energy to establish themselves as international exporters.
➣ Competitive Analysis
➣ Recent Development
March 1st 2024, Yara, a leading Norwegian crop nutrition company and a global leader in ammonia trade and shipping, and GHC SAOC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Acme Cleantech, a leading renewable energy company in India, today signed a firm and binding agreement for supply of ammonia with reduced CO2 emissions from Acme to Yara on a long-term basis.
May 25th 2022, LSB Industries, Inc. announced that it entered into agreements with ThyssenKrupp Uhde USA, LLC and Bloom Energy, to develop a project to produce approximately 30,000 metric tons of zero-carbon or “green” ammonia per year at LSB’s Pryor, Oklahoma facility (“Pryor”). Green ammonia is produced by extracting hydrogen from water using an electrolyzer powered by a renewable energy source, such as solar or wind. Since no natural gas or other fossil fuels are used as the feedstock to the ammonia production process, nor as the power source, the end-product has no associated carbon emissions.
➣ Industry Dynamics
➣ Industry Drivers
Decarbonization and Climate Goals
Meeting global climate targets has made decarbonization a top priority, especially for sectors like ammonia production that mostly depend on carbon-intensive operations. Conventional ammonia production techniques, such the Haber-Bosch process, need a lot of energy and mostly fossil fuels, which results in considerable carbon emissions. The objectives of the Paris Agreement, which aim to keep global warming far below 2°C, ideally 1.5°C, above pre-industrial levels, are at odds with conventional ammonia production because of this dependency.
A possible, carbon-neutral substitute is green ammonia, which is generated from renewable energy sources like hydropower, solar power, or wind. The production process for green ammonia can reduce carbon emissions by employing green hydrogen produced from water electrolysis driven by renewable energy, supporting national and corporate decarbonization goals. Thus, switching to green ammonia is in line with the climate objectives of numerous countries and businesses that are dedicated to reaching net-zero emissions by 2050 or earlier.
Green ammonia adoption can drastically lower carbon footprints for supply chains in the energy, maritime, and agricultural sectors—all of which are major users of ammonia and products generated from it. Green ammonia can also function as a flexible energy transporter, possibly facilitating hydrogen transfer and energy storage. Green ammonia's importance in the shift to sustainable energy systems is further enhanced by its adaptability, which establishes it as a vital component of international efforts to meet climate and decarbonization goals.
➣ Industry Restraint
The expansion of green ammonia production and the improvement of its cost competitiveness depend heavily on technological developments in electrolysis technology. Efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness have been significantly improved using Alkaline Water Electrolysis (AWE), Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis (PEM WE), and Solid Oxide Electrolysis (SOE). With improved catalysts and materials that increase operating life and boost energy conversion efficiency, AWE—which is renowned for its durability and affordability—is developing. PEM WE is gaining from advancements in membrane materials and electrode architectures, which improve performance and lower prices, thanks to its quick reaction times and small size. With advancements in electrochemical materials and system integration, SOE—which can use waste heat and runs at high temperatures—is becoming more efficient overall. These technological strides are making electrolysis-based green hydrogen production more economically viable, directly contributing to the competitiveness of green ammonia, which is essential for decarbonizing agriculture, energy, and other industries.
➣ Industry Restraint
Green ammonia production is now more costly than regular ammonia, mostly because of the high expenses of infrastructure, electrolysis equipment, and renewable energy. Green ammonia is created by electrolyzing water to produce hydrogen using renewable energy sources like sun or wind. The infrastructure for renewable energy and the electrolysis apparatus both require a significant amount of capital. Electrolyzers, particularly those used in Solid Oxide Electrolysis (SOE) and Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM), are expensive initially because they need sophisticated materials and great precision to function effectively. Further complexity and expense are added when these electrolyzers are integrated with ammonia synthesis facilities, such as the Haber-Bosch process. While renewable energy costs are decreasing, they remain a significant factor in the overall expense of green ammonia. This makes large-scale commercialization difficult without substantial subsidies or reductions in technology costs. As innovations continue and economies of scale are realized, these costs are expected to decrease, making green ammonia more competitive with traditional ammonia.
➣ Report Scope
The report includes Global & Regional market status and outlook for 2017-2028. Further, the report provides break down details about each region & countries covered in the report. Identifying its sales, sales volume & revenue forecast. With detailed analysis by types, applications. The report also covers the key players of the industry including Company Profile, Product Specifications, Production Capacity/Sales, Revenue, Price, and Gross Margin 2017-2028 & Sales with a thorough analysis of the market’s competitive landscape and detailed information on vendors and comprehensive details of factors that will challenge the growth of major market vendors.
|
Attributes |
Details |
|
Segments |
By Type
By Application
|
|
Region Covered |
|
|
Key Market Players |
|
|
Report Coverage |
|